Antibiotic resistance
- Property of microbe
- Defined as micro-organism not inhibited by the usually achievable systemic concentration of an AMA with normal dosage schedule and / or fall in the MIC range.
Multi Resistance
- MDR –non-susceptibility to at least 1 agent in 3 antimicrobial categories
- XDR – non-susceptibility to at least 1 agent in all but susceptible to 2 or fewer antimicrobial categories
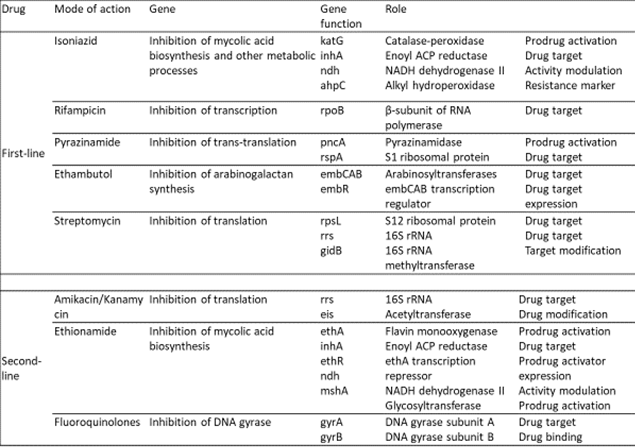
Initially, the term XDR was created to describe extensively drug-resistant Mycobacterium tuberculosis (XDR MTB) and was defined as ‘resistance to the first-line agents’ isoniazid and rifampicin, to a fluoroquinolone and to at least one of the three-second-line parenteral drugs (i.e. amikacin, kanamycin or capreomycin)’. Subsequent to this, definitions for strains of non-mycobacterial bacteria that were XDR
- Pan-drug-resistant (PDR) – Non-susceptibility to all agents in all antimicrobial categories
Cross Resistance
Acquisition of resistance to one AMA conferring resistance to another AMA, to which the organism has not been exposed.
- Between chemically related drugs.
Eg. Aminoglycoside-modifying enzymes which may confer resistance to several members of the aminoglycoside family.
- Unrelated drugs may show partial cross-resistance: a result of either overlapping drug targets
Eg. Macrolides and Lincosamides
Impact of antibiotic resistance
- Longer duration of illness
- Longer treatment
- Increased mortality
- Huge economic impact
- Patients to community and health care worker
- Negates advances in healthcare
Three agents of greatest concern associated with both hospital- and community-acquired infections.
- E-coli
- Klebsiella pneumonia
- Staphylococcus aureus
- Methicillin-Resistant Staphylococcus Aureus (MRSA)
- Extended-Spectrum Beta-Lactamase (ESBL)
– Enterobacteriaceae
– Acinetobacter baumanni
- Carbapenem resistance
– Enterobacteriaceae
- Non-fermenting gram-negative bacilli (NFGNB)
- Vancomycin-Resistant Enterococcus (VRE)
Other Infections
- Kala-azar
– 60% resistance in pentavalent antimony
– 25% in pentamidine
- Typhoid
fever
- MDR Salmonella Typhi prevalent all over
- FQ resistance in Salmonella typhi, 8% in 2008 to 24% in 2014
- Vibrio cholerae
- resistance to furazolidone, cotrimoxazole, nalidixic acid
- Tetracycline remains effective
- A recent study in Sikkim, India found that MRSA was seen in 39% clinical specimens of S. aureus
What is NDM-1?
- New Delhi Metallo-beta-lactamase-1 (NDM-1) first described by Yong et al in 2009
- The gene for NDM-1 is a member of a large gene family that encodes beta-lactamase enzymes called carbapenemases.
- Bacteria that produce carbapenemases – superbugs
- NDM-1 was first detected in a Klebsiella pneumoniae isolate from a Swedish patient of Indian origin in 2008
- Susceptible to a few antibiotics (polymyxins, colistin)
Superbugs* are visible manifestations of our prolonged failure to preserve antibiotics
(** Methicillin-resistant Staph aureus, MDR-and XDR Mycobacteria, ESBL producing Gram-negative bacteria and NDM-1 producing Enterobacteriaceae bacteria are few examples of superbugs because these fail to respond to a large number of commonly used antibiotics)
Causes:
Known but inevitable
- A continuous natural evolution of resistance in bugs
Known but neglected à Need immediate action
- Accumulation of resistance to multiple antibiotics
- Self-medication and poor compliance
- Inappropriate use of antibiotics selection & multiplication of resistant strains
- Weak surveillance & regulatory systems
Factors of Antibiotic Resistance
Patient-Related causes
- Poor adherence of dosage regimens
- Lack of education
- Self-medication
- Misconception
Drug-related causes
- Counterfeit substandard drugs
- Irrational FDC of antimicrobials
- Over the counter availability of drugs
- Poor regulatory control
- Soaring use of antibiotics
Prescriber related factors
- Lack of current knowledge and training
- Inappropriate use of available drugs
- Overuse of antimicrobials
- Inadequate dosing
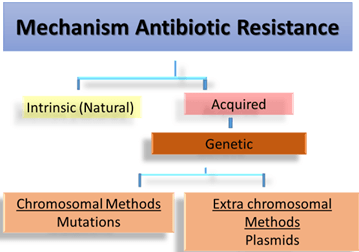
Intrinsic mechanism
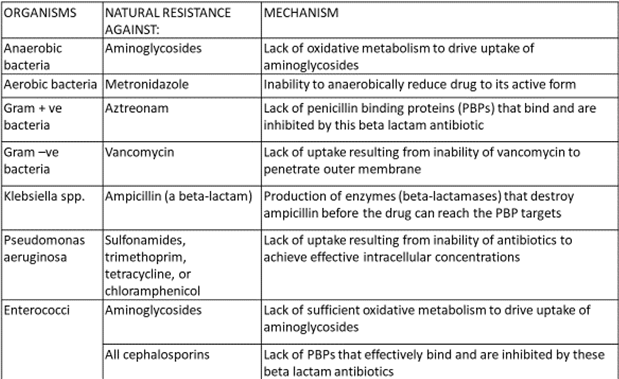
- Innate ability – to resist the activity of a particular antimicrobial agent through its inherent structural or functional characteristics
- No clinical significance, only proper drugs to be selected
Acquired mechanism of resistance
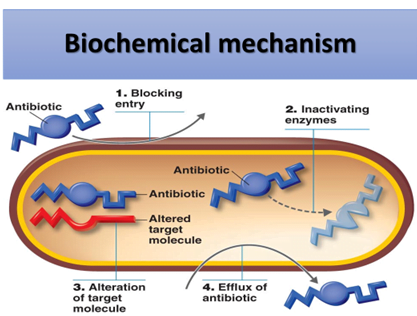
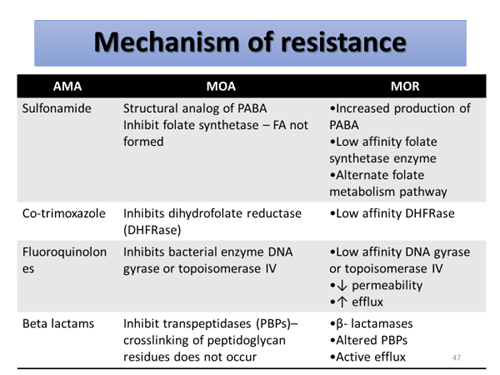
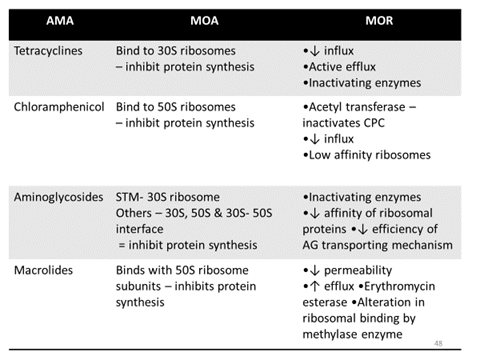
By the production of enzymes that inactivates the antibiotic.
- Beta lactamase enzyme – beta lactam antibiotics (S. aureus, N. gonorrhea, H. influenza)
- Chloramphenicol acetyl transferase – chloramphenicol (gram –ve > gram +ve)
- Acetyl transferases, phosphotranferases and adenyltransferases – aminoglycoside
Prevention of drug accumulation in the bacterium
- Efflux pump – cytoplasmic membrane
transport proteins
- E.coli, P.aeruginosa, S. typhi, S. aureus, S. pneumonia etc.
- A major mechanism of resistance for tetracycline, increasing for FQ’s
- Inhibition of plasmid-mediated synthesis of porin channels – obstruct influx of hydrophilic penicillin. Eg. ampicillin
Modification of target sites
- Altered DNA gyrase – FQ
- Altered PBP in Strep. Pneumoniae – Penicillin
Use of alternative pathway for growth requirement
- Bypass the reaction inhibited by the antibiotic
- Eg. Sulfonamide resistance
– Alternate folate metabolism pathway
– overproduction of PABA
Quorum sensing
- Mode of communication with each other and exchange signaling chemicals (Autoinducers)
- Allow bacteria to coordinate gene expression for virulence, conjugation, apoptosis, mobility, and resistance
- But when? its colony reaches a critical density (quorum), a threshold of autoinduction is reached and gene expression starts
- QS signal molecules: AHL, AIP, AI-2 & AI-3
- QS inhibitors – synthesized and isolated from several natural extracts such as garlic extract.
Genetic mechanisms
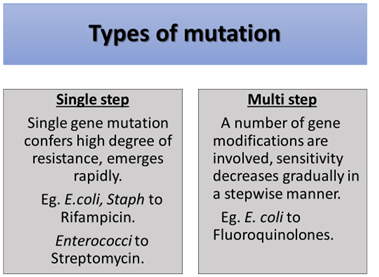
- Chromosomal Mutation
- Spontaneous change in the DNA structure of the gene
- Low mutation rate – frequency is 1/mln cells
- Over the course, sensitive bacteria die and resistant survive and multiple
Extrachromosomal mechanism: Plasmids
- Carry resistant genes to antibiotics (r – genes) aka R- plasmids
- Transferred from one R- plasmid to another plasmid or chromosome.
- Horizontal gene transfer
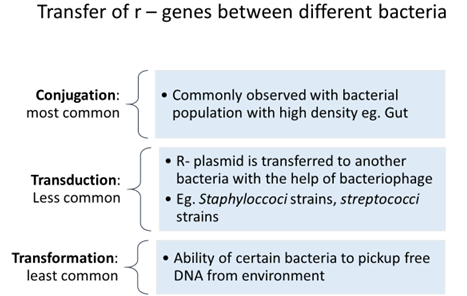
Transfer of r – genes between plasmids within the bacterium
- Transposons – mobile genetic
elements that can move anywhere in a genome and transfer
r – genes between plasmids or from plasmid to chromosome.
- Transposons co-integrate with acceptor plasmid and replicate
- Integrons – Larger mobile genetic elements
- packed with multiple gene cassettes each containing r- gene
- It cannot promote self-transfer like transposons.
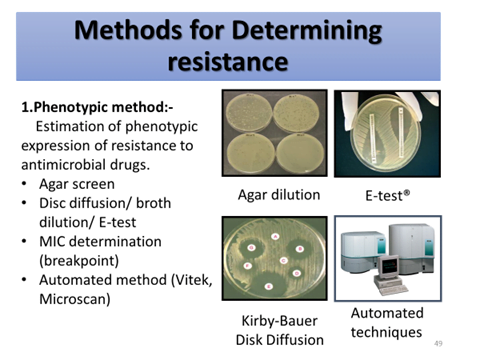
2.Genotypic method:-
Detection of genes or nucleotide sequences responsible for coding resistance.
- DNA hybridization
- Nucleic acid amplification (PCR) technique
- Microarray techniques
How to overcome antimicrobial resistance
- Judicious use of use antibiotics
- Develop new antibiotics à Bypass the drug resistance
- Other options
Antibiotic stewardship
- A program that encourages judicious use of antibiotics
- Multidisciplinary team –
- New drug development
- Surveys and audits
- Formulating STG, Policies for use of AB in hospital, for govt.
- Keeping formulary up-to-date
- Essential drug list
Antibiotic stewardship at the community level
- Avoid further development of resistance
- Multidisciplinary team
- Generate public awareness – drug resistance, imp. of vaccination, hygiene in preventing infection
- Interventions to improve antibiotic prescribing – CME, educational sessions, antibiotic prescription charts, hospital antibiograms
- Conduct surveys and prescription audit with feedback
- Formulate policies – hospital and national use to Curb misuse of AMA, control the spread of infection and save money
Initiatives taken by India with respect to AMR
- The National Policy for Containment of Antimicrobial Resistance (2011)– not yet implemented.
– Strategy to monitor the sale of antibiotics (misuse, overuse), AMR surveillance (lab), promote research, measures to enhance rational use of antibiotics in hospital and curb its use in veterinary and industry - 12th Five Year Plan- Containment of AMR (2012 – 2017) – create awareness for rational use of antibiotics among health care providers and common people
- The Drugs and Cosmetic Rule, 1945 was amended in 2013 to include a new Schedule H1.
- 46 drugs Sold only with the prescription of RMPThe drug should be labeled with the symbol Rx in red and warning
- National Anti-Microbial Resistance Research and Surveillance Network (AMRRSN) (ICMR) (2015) – to compile national data of AMR at different levels of Health Care
- National Treatment Guidelines for Antimicrobial Use in Infectious Diseases (2016 v1)
- ICMR – Treatment Guidelines for Antimicrobial Use in Common Syndromes
- The Union Health Minister launched a campaign called “Medicines with the Red Line” – promote rational use
