Medical Biotechnology is the use of living cells and cell materials to research and produce pharmaceutical and diagnostic products that help treat and prevent human diseases.
Applications
- INSULIN PRODUCTION
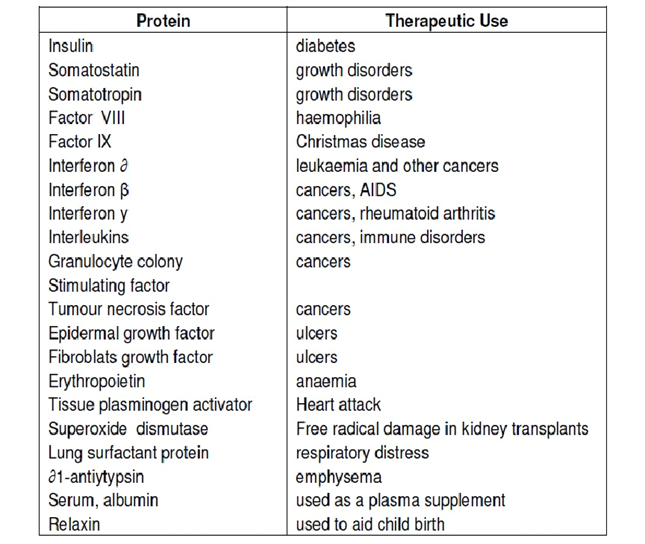
- Production of genetically engineered human insulin was one of the first breakthroughs of biotechnology in the pharmaceutical industry.Insulin was first produced in Escherichia coli through recombinant DNA technology in 1978. PRINCIPLE:- Mass production of human proteins, vaccines, etc. by genetically modifying bacteria or viruses.PROCESS:- The human gene for insulin is placed into bacteria, are cultured and allowed to produce insulin which is collected, purified and sold to diabetics worldwide.
- HUMAN GROWTH HORMONE
- Production of human growth hormone was first done in 1979 using recombinant DNA technology.
- scientists produced human growth hormone by inserting DNA coding for human growth hormone into a plasmid that was implanted in Escherichia coli bacteria.
- This gene that was inserted into the plasmid was created by reverse transcription of the mRNA found in pituitary glands to complementary DNA.
- Prior to this development, the human growth hormone was extracted from the pituitary glands of cadavers, as animal growth hormones have no therapeutic value in humans.
- HUMAN BLOOD CLOTTING FACTOR
- Production of human clotting factors was enhanced through recombinant DNA technology.
- Human clotting factor IX was the first to be produced through recombinant DNA technology using transgenic Chinese hamster ovary cells in 1986.
- Plasmids containing the factor IX gene, along with plasmids with a gene that codes for resistance to methotrexate, were inserted into Chinese hamster ovary cells via transfection.
- GENE PILL
- Gene pill delivers DNA to Intestine
- DNA is absorbed by gut cells
- Protein drug is synthesized inside the cells
- Protein drug is secreted into the blood
- MONOCLONAL ANTIBODIES (MAB)
Steps in making them:
- Human antibody genes are put into a mouse.
- The mouse is infected causing it to make human antibody-producing cells (B-cells).
- These cells are removed from the mouse and fused with a tumor cell.
- Now we have a tumor cell that is constantly producing antibodies and more cells like itself
GENE THERAPY
- Gene therapy is the use of DNA as a pharmaceutical agent to treat disease.
- It derives its name from the idea that DNA can be used to supplement or alter genes within an individual’s cells as a therapy to treat disease
- The most common form of gene therapy involves using DNA that encodes a functional, therapeutic gene to replace a mutated gene.
- Gene therapy is of two types, somatic gene therapy, and germline gene therapy.
SEVERE COMBINED IMMUNE DEFICIENCY (ADA-SCID)
- ADA-SCID is also known as the bubble boy disease.
- Affected children are born without an effective immune system and will succumb to infections outside of the bubble without bone marrow transplantation from matched donors.
- The therapeutic gene called ADA was introduced into the bone marrow cells of such patients in the laboratory, followed by transplantation of the genetically corrected cells back to the same patients.
- The immune system was reconstituted in all six treated patients without noticeable side effects, who now live normal lives with their families without the need for further treatment.
CHRONIC GRANULOMATUS DISORDER (CGD)
- CGD is a genetic disease in the immune system that leads to the patients’ inability to fight off bacterial and fungal infections that can be fatal.
- Using similar technologies as in the ADA-SCID trial, investigators in Germany treated two patients with this disease, whose reconstituted immune systems have since been able to provide them with full protection against microbial infections for at least two years.
HEMOPHILIA
- Patients born with Hemophilia are not able to induce blood clots and suffer from external and internal bleeding that can be life-threatening.
- The therapeutic gene was introduced into the liver of patients, who then acquired the ability to have normal blood clotting time.
Multiple gene therapy strategies have been developed to treat a wide variety of acquired diseases like
- Cancer, Parkinson’s Disease, Huntington’s Disease, Influenza, HIV, Hepatitis
Stem Cells
- A stem cell is a cell that has the potential to become any cell type in the human body.
- The easiest place to get stem cells is from an embryo.
- Stem cells are introduced into a damaged area of the body where, under the right conditions, they will replace the damaged area.
Stem cell sources-
- Embryonic stem cells
- Infant and adult stem cells
- Present in small numbers in
- Bone marrow
- Peripheral blood
- Skin epithelium
- Umbilical cord blood
- The dental pulp of infant’s teeth
- May be obtained by reprogramming somatic cells
- Introduction of retroviruses carrying reprogramming genes into fibroblasts
- Present in small numbers in
Application –
The main areas where stem cells have proven their worth is in bone marrow transplants, replacing damaged heart tissue after a heart attack and replacing damaged nerve tissue which gives hope to anyone who has had a spinal cord injury
