Irritable Bowel Syndrome
According Rome IV criteria, Irritable bowel syndrome (IBS) Recurrent abdominal pain, averaging ≥ 1 day/week, in last 3 months, with ≥ 2 of the following criteria:
- Related to defecation
- Associated with a change in frequency of stool
- Associated with change in form (appearance) of stool.
Pathophysiology
- Innate/Acquired host-related factors
- Psychiatric illness
- Life stressors
- Intestinal permeability.
- Bile Acid malabsorption
- Immune function.
Altered colonic & small bowel motility à High-amplitude propagated contractions (HAPCs) à Enhanced gastro-colic response à Rectal hypersensitivity à Diarrhea
Increased segmental (non-propulsive) contractions àDecreased HAPCs èReduced rectal sensation à Rectal hyposensitivity à Constipation
Clinical Features
- Bloating, Pain, Abdominal distention
- Abnormal stool form (hard &/or loose)
- Abnormal stool frequency
- Straining at defecation
- Urgency
- Feeling of incomplete evacuation
- Passage of mucus per rectum
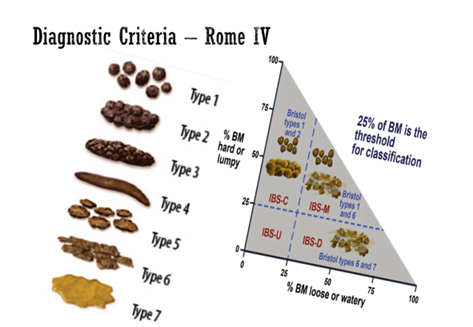
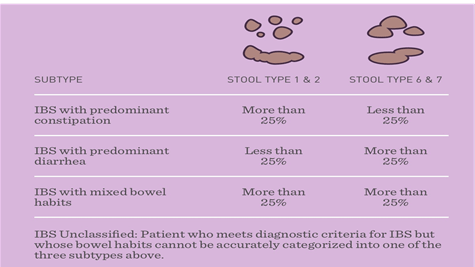
Types Of IBS
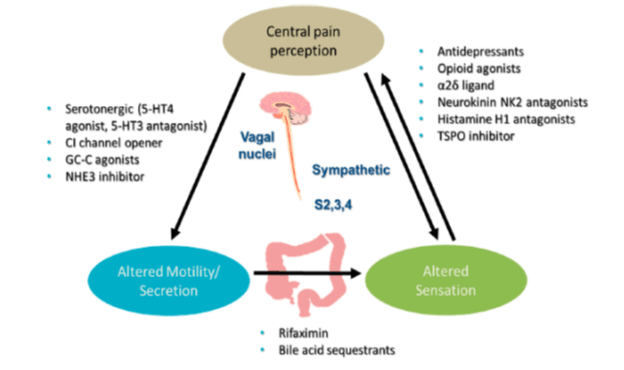
Pharmacotherapy
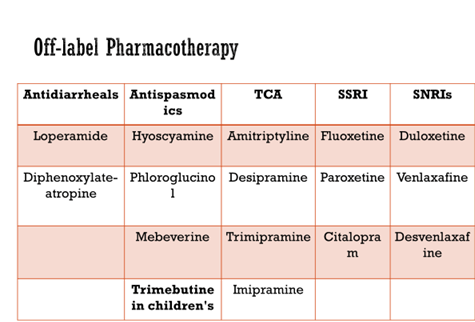
Antispasmodics
- Hyoscyamine, Dicyclomine – Block muscarinic acetylcholine receptors, causing smooth muscle relaxation
- Peppermint oil capsules, enteric coated – Calcium-channel blocking activity, leading to smooth muscle relaxation NNT = 3
- Phloroglucinol
- Mebeverine – Sodium-channel blocking activity,
- Trimebutine – Peripheral μ-, κ-, and δ-opioid receptor agonist
Lifestyle Changes & Dietary Alterations
- Diary card symptom tracking help identify exacerbating & alleviating factors & increase sense of control
- Moderate exercise for 20 – 60 min x 3 to 5 days/week improves IBS symptoms
- Low-fat diet
- Diet low in fermentable oligosaccharides, disaccharides, monosaccharides, & polyols (FODMAPs) – IBS-D
Nonpharmacologic Psychological Therapies
- Cognitive Behavioral Therapy (CBT)
- Hypnotherapy
- Multicomponent Psychological Therapy
- Dynamic Psychotherapy
- Significantly more effective than usual management, supportive therapy, or placebo in patients with IBS,
- With an overall – NNT = 4
IBS-D à ARRE (Alosetron, Ramo, Rifaximin, Eluxadoline)
Alosetron
- Selective 5-HT3 antagonist that reduces abdominal pain & bowel movement (BM) frequency & urgency
- Indicated only in WOMENS with more severe IBS-D who have inadequate response to conventional therapy
- Starting dose – 0.5 mg BD & increased up to 1mg BD
- A/E- Constipation, abdominal discomfort
- Blackbox Warning: Discontinue in patients who develops Constipation & Ischemic Colitis.
- Initial U.S. Approval: 2000 then in 2008 – LOTRONEX should be discontinued in patients who have not had adequate control of IBS symptoms after 4 weeks of treatment with 1 mg twice a day. Available under a specific risk management program
Ramosetron
- 5-HT3 antagonist
- In Japan Ramosetron used in treatment of IBS-D in both men & women
- Response rates respectively of 47% to 51%, compared with 27% to 32% with placebo (p < 0.001)
- A/E- Constipation, abdominal discomfort
Eluxadoline — 2015
- Mixed μ-opioid & κ-opioid receptor agonist, & δ-opioid antagonist that is locally active in GI tract
- 75 or 100 mg BID. indicated in adults for IBS-D
- AEs – Constipation, Nausea, & Abdominal pain: ~7–9% of patients
- Lower dose of 75 mg BID in patients who are post cholecystectomy
- C/I- Patients with history of alcohol abuse or addiction
- FDA warns increased risk of serious pancreatitis with drug eluxadoline in patients without gallbladder
Rifaximin — 2015
- Semi-synthetic derivative of rifampin & acts by binding to bacterial DNA-dependent RNA polymerase blocking & steps in transcription
- Non-systemic antibiotic – 550 mg TDS
- NNT = 10.6 & NNH = 8971
- A/E- Nausea (3%) & Increased ALT (2%).
- No reports C. difficile or drug-resistant bacteria
IBS- C (SPELL PTT)
Lubiprostone — 2006
- Chloride channel activator – intestinal fluid secretion, Increases motility, thereby facilitating passage of stool & alleviating symptoms associated with constipation
- Indication: 8-mcg capsule for IBS-C in women ≥ 18yr
- A/E- Nausea & Diarrhea
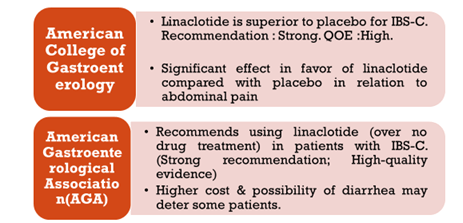
Linaclotide
- FDA approved in 2012 for IBS-C
- Guanylate cyclase-C (GC-C) agonist, Increase in cGMP, Secretion of Cl & HCO3 into gut, through activation of (CFTR) ion channel, resulting in increased intestinal fluid & accelerated transit.
- Indication: 290 mcg (5 mcg/kg/d) OD in both men & women
- A/E: Diarrhea (2%), Abdominal Pain.
- Black box warning – Risk of serious dehydration in pediatric patient, C/I in <6yr age, Avoid use in 6yr to less than 18yr.
Plecanatide
- U.S. FDA Approval: 2018
- Guanylate cyclase-C (GC-C) agonist, increase in cGMP, Secretion of Cl & HCO3 into intestinal lumen, through activation of (CFTR) ion channel, resulting in increased intestinal fluid & accelerated transit.
- 3mg(0.05 mg/kg/d) OD indicated in adults IBS-C
- M/C adverse reaction is diarrhea >2%.
- Black box warning – Risk of serious dehydration in pediatric patient, C/I in <6yr age. Avoid use in 6 to < 18yr.
TeNapanor
- Ardelyx will file NDA with 2 successful phase 3 trials
- NHE3 inhibitor-to reduce absorption of Na+, leading to increased Na+ within gut causing retention of fluid in gut, loosening stool,
- Primary endpoint- Combined responder rate for 6 of 12 weeks, tenapanor vs. placebo.
- at least 30 percent reduction in abdominal pain,
- increase of one or more complete spontaneous bowel movements (CSBM) in same week.
Elobixibat
- Inhibitor of ileal bile acid transporter (IBAT), is safe & effective for treating chronic constipation
- Blocking enterohepatic circulation of bile acids, increasing bile acid concentration in gut, which accelerates intestinal passage & softens stool.
- (5mg) BD – Indicated for Chronic Constipation in Japan.
- Once‐daily administration safe & tolerated up to 20 mg in female & male patients with CC
Serum-derived Bovine Immunoglobulin
- Helps to maintain immune balance & gut barrier function.
- Placebo-controlled pilot study showed significant decrease in abdominal pain, flatulence, bloating, urgency, loose stools, & total days with IBS symptoms.
- SBI exhibited similar safety profile to placebo.
- One patient survey suggest that SBI use
- Clinically relevant decreases in daily stool frequency
- Improvements in overall management of their condition & aspects of QoL.
EC-Peppermint Oil
- Reduce GI smooth muscle motility by acting as calcium antagonist
- Triple-coated microsphere formulation to facilitate SR in small intestine, & to reduce AEs associated such as heartburn, abdominal pain, or anal burning
- Dose = 0.6 mL TDS
- 4-week, placebo controlled trial significant improvement in abdominal pain/discomfort, bloating, urgency, & pain at evacuation in IBS-D & IBS-M
Tong-Xie-Yao-Fang Granules
- TXYF granules consist 4 herbal products: – Decreases elevated colon smooth muscle tension & spontaneous activity & also downregulate 5-HT & SP.
- Significantly higher rate of relief of global symptoms in TXFY group during weeks 1 to 4
- M-TXYF was significantly superior to routine pharmacotherapies (RP) in clinical therapeutic efficacy (NNT) = 5.7)
- Significantly reduce scores of abdominal pain abdominal distention, diarrhea, & frequency of defecation.
