Therapeutic Drug Monitoring
- Definition à clinical laboratory measurement of a chemical parameter that, with appropriate medical interpretation, will directly influence drug prescribing procedures.
- TDM refers to the individualization of drug dosage maintaining plasma or blood drug concentrations within a targeted therapeutic range or window.
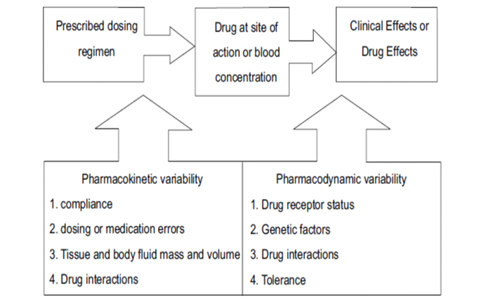
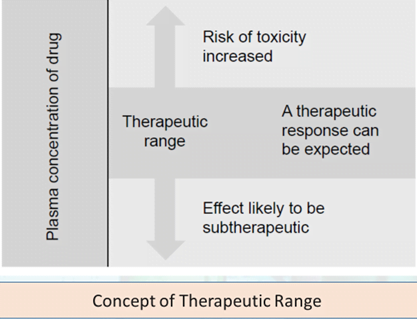
TDM will be useful if :
1) Narrow therapeutic range
2) Direct relationship between the drug or drug metabolite levels in plasma and the pharmacological or toxic effects
3) Therapeutic effect cannot be readily assessed by the clinical observation
4) Large individual variability in steady state plasma concentration exists at any given dose
5) Appropriate analytic techniques available to determine the drug and metabolite levels.
Indication of TDM:
- Monitoring compliance
- Individualizing therapy à during early therapy and during dosage changes
- Diagnosing under-treatment
- Avoiding toxicity
- Monitoring and detecting drug interactions
- Guiding withdrawal of therapy
Steady State– Equilibrium between the amount of drug given and the amount eliminated over the dosing interval.
- Takes a drug 4-5 half-lives to reach a steady state.
- Sampling should occur when the drug has reached its steady state to judge efficacy and toxicity of the drug therapy.
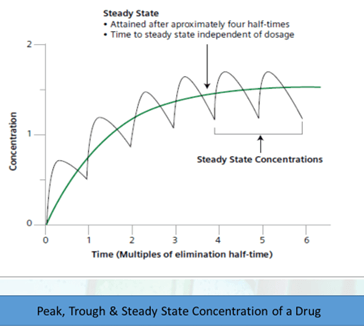
Trough– Lowest drug concentration during a dosing interval when drug is given intermittently.
- The trough concentration occurs immediately before administration of the next dose.
Peak– Highest serum drug concentration that occurs following a single dose or at steady state within a dosing interval.
Laboratory Investigations & TDM
Associated investigations help to detect factors which may elevate toxicity. … t3/T4 why??
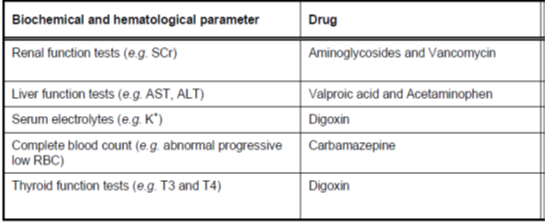
Drugs for TDM
| Class of Drug | Examples |
| -Cardiac Drugs | Digoxin, Amiodarone |
| -Anti Epileptic Agents | Phenytoin, Carbamazepine, Valproic Acid |
| -Antibiotics | Gentamycin, Vancomycin |
| -Antidepressants & Antipsychotics | Lithium, Tricyclic Antidepressants |
| -Analgesics | Acetaminophen, Aspirin |
| -Anti-cancer Drugs | Methotrexate |
| -Bronchodilators | Theophylline |
| -Immunosuppressant | Cyclosporine |
| Drug | Therapeutic Range |
| Digoxin | 0.8-2 ug/L |
| Lithium – Acute Mania – Maintenance | 0.8-1.2 mmol/L 0.4-1.0 mmol/L |
| Phenytoin | 10-20 mg/L |
| Sodium Valproate | 50-100 mg/L |
| Carbamazepine | 5-12 mg/L |
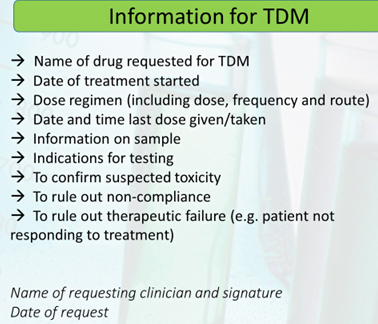
Analysis methods should ideally:
- Distinguish between compounds of similar structure
- Detect small amounts.
- Be Simple enough to be used routinely
- Be Unaffected by other drugs administered.
Various Methods for TDM
- HPLC (High Performance Liquid Chromatography)
- Spectrophotometry
- RadioImmunoAssay (RIA)
- Enzyme Immuno Assay (ELISA)
TDM – The Cost Factor
- Cost à sum of equipment, personnel, supply and overhead expenditure for a given period of time and dividing that amount by the number of assays performed in the same time interval.
- A pharmaco-economic analysis of the impact of TDM in adult patients with generalized tonic-clonic epilepsy showed that patients undergoing TDM had much more effective seizure control, fewer adverse events, better earning capacity, lower costs to the patient and savings from lower hospitalizations per seizure.
Future Application of TDM
- Individualisation of treatment
- Combining with Pharmacogenomics
- Better assay methods/Trained Technicians
