Phosphodiesterase Inhibitors
- A phosphodiesterase is any enzyme that breaks a phosphodiester bond.
- There are many other families of phosphodiesterases, including phospholipases C and D, autotaxin, sphingomyelin phosphodiesterase, DNAses, RNAses, and restriction endonucleases
- Usually, people speaking of Phosphodiesterase are referring to cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases, which have great clinical significance.
- The cyclic nucleotide phosphodiesterases comprise a group of enzymes that degrade the phosphodiester bond in the second messenger molecules cAMP and cGMP.
- PDEs are therefore important regulators of signal transduction mediated by these second messenger molecules.
Historical aspects
- The phosphodiesterase (PDE) story begins with the work of Henry Hyde Salter in 1886
- An asthmatic he noted that when he drank a strong cup of coffee on an empty stomach, his breathing eased, an effect attributed to the bronchodilator properties of caffeine
- Although the mechanism of action at the time was unknown, it has since been shown that caffeine was acting as a non-selective PDE inhibitor
The classification is based on:
- PDE substrate specificities by enzyme family
- Some are cAMP selective hydrolases(PDE 4, 7 and 8)
- cGMP selective(PDE 5, 6 and 9)
- Hydrolyse both cAMP and cGMP (PDE 1, 2, 3, 10,11)
- Amino acid sequences
- Regulatory properties
- Tissue distribution
- Nonselective phosphodiesterase inhibitors
Methylated xanthines and derivatives:
- Caffeine
- Aminophylline, Theophylline –
- Inhibition of phosphodiesterase (PDE) isozymes
- Antagonism of adenosine receptors
- Inhibition of calcium influx
- Enhancement of catecholamine secretion
- Smooth muscle – relaxant
- Reduced activity of inflammatory cells
- Oral theophylline used in patients of COPD and mild to moderate asthma act synergistically with β 2 agonists in asthma
- ADR
- Nausea, Vomiting, headache -PDE 3 inhibition
- Gastric discomfort- PDE 3 inhibition
- Diuresis- Adenosine antagonism
- Cardiac arrythmias -PDE 3 inhibition
- Seizures- Adenosine antagonism
- Narrow margin of safety
- Therapeutic range – 8-15 mcg/ml
- Theobromine
- Pentoxifylline
- Theobromine analogue
- Inhibits PDE enzyme Reduces blood viscosity and improves blood flow in ischemic area through microcirculation
- Uses:
- One of the DOC for PVDs
- Non hemorrhagic stroke
- Chronic cerebrovascular insufficiency
- Trophic leg ulcers
- Dose: 400 mg BD orally
Selective PDE inhibitors.
| PDE | DRUGS |
| PDE 1 | Vinpocetine |
| PDE 2 | EHNA |
| PDE 3 | Anagrelide,Cilostamide, Milrinone, Cilostazol ,Dihydro-pyridazinone |
| PDE 4 | Rolipram ,Denbufylline, Cilomilast,Roflumilast,ibudilast,leuteolin |
| PDE 5 | Sildenafil (Viagra), Zaprinast, Dipyridamole, Vardenafil, Tadalafil |
| PDE 6 | Zaprinast, Dipyridamole, Vardenafil, Tadalafil |
| PDE 7 | Dipyridamole |
| PDE 8 | Dipyridamole |
| PDE 9 | Zaprinast |
| PDE 10 | Dipyridamole, Papaverine |
| PDE 11 | Tadalafil, Zaprinast, Dipyridamole |
PDE 1 inhibitor – Vinpocetine
- Semisynthetic derivative alkaloid of vincamine, an extract from the periwinkle plant
- It increases cerebral blood flow and is said to improve memory
USE:
- As vasodilator
- many performance-enhancing supplements to improve delivery of nutrients to muscles after physical workouts
- Anti-inflammatory agent
PDE 2 inhibitor EHNA (erythro-9-(2-hydroxy-3-nonyl) adenine)
- Inhibition of PDE2 by EHNA potentiates NMDA receptor activated increase in cGMP, but has no effect on cAMP concentrations
- Also EHNA is a potent inhibitor of adenosine deaminase. This dual inhibition (PDE plus ADA) leads to the accumulation of the two inhibitory metabolites, adenosine and cGMP, which may act in synergy to mediate diverse pharmacological responses including anti-viral, anti-tumour and antiarrhythmic effect
USE:
- Study implication of PDE2 in calcium control in cardiac myocytes
- Shown to be effective to reverse hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction in perfused lung models
PDE 3 inhibitor – Anagrelide
- Drug used for the treatment of essential thrombocytosis or overproduction of blood platelets.
- Also has been used in the treatment of chronic myeloid leukemia
Mechanism of action:
- Inhibiting the maturation of platelets from megakaryocytes inhibitor of phosphodiesterase-II.
- It inhibits PDE-3 and phospholipase A2.
Uses:
- Combination of anagrelide and aspirin for the initial management of ET
ADRs:
- Headache, diarrhea, unusual weakness/fatigue, hair loss, nausea and dizziness.
- Less common side effects include: congestive heart failure, myocardial infarction, cardiomyopathy
Contraindications
- Severe hepatic function impairment.
- Dose:0.5 mg /day
- Inamrinone, Milrinone — Mechanism of action:
- Selectively inhibits PDE 3, located in heart à Increased cAMP
- Enhances relaxation of the left ventricle by increasing Ca++-ATPase activity on the cardiac sarcoplasmic reticulum which increases calcium ion uptake
- Positive ionotropic on heart
- Vasodilatation of vessels (Ionodilator)
- used in the management of heart failure only when conventional treatment with vasodilators and diuretics has proven insufficient due to the potentially fatal adverse effects of milrinone, including ventricular arrhythmias
- Prolonged half-life (2.5 hrs) àThis can result in a prolonged weaning and possible adverse outcomes from stopping this medication rapidly.
- Only used IV for acute heart failure cases, dihydropyridazinone àfirst orally active, potent, and selective PDE3B inhibitor.
Cilostazol
- selective inhibitor of 3-type phosphodiesterase (PDE3) à increasing cAMP.
- An increase in cAMP à increase in the active form of Protein kinase A , which is directly related with à inhibition in platelet aggregation.
- PROTEIN KINASE also prevents the activation of an enzyme (myosin light-chain kinase) that is important in the contraction of smooth muscle cells, thereby exerting its vasodilatory effect.
- Use:
- Used as an antiplatelet agent mainly in intermittent claudication
- Adjuvant antianginal agent
- Used off-label for treatment of intracranial atherosclerosis and secondary stroke prevention
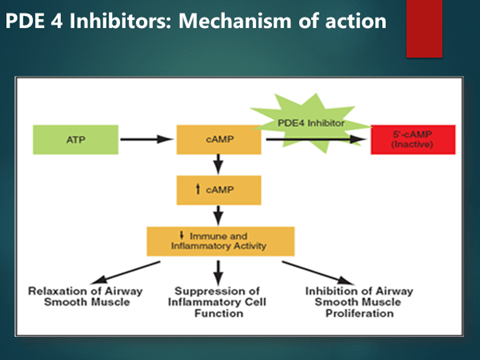
Rolipram
- Antidepressant compound
- The high selectivity of rolipram, for PDE4 was demonstrated on vascular purified PDE
- Therefore rolipram became an archetype to synthetize new potent and selective PDE4 inhibitors
- improves deficits in both long-term potentiation (LTP) and contextual learning in the double transgenic mice for amyloid precursor protein
- suggesting that PDE4 inhibitor would be effective in Alzheimer disease
- Rolipram mainly used as investigative tool in pharmacological research
Roflumilast, Cilomilast:
- Selective PDE 4 Inhibitors
- indicated for people with severe COPD to prevent symptoms such as coughing and excess mucus from worsening
Dosage:
- 500 μ g/day oral alone or in combination with β 2 agonist
ADRs: Nausea, vomiting, Headache, nasopharyngitis, URTI, decreased appetite
Ibudilast :
a neuroprotective and bronchodilator drug used mainly in the treatment of asthma and stroke.
Drotaverine
- Novel PDE 4 inhibitor
- Elevated cAMP leads to relaxation of smooth muscles of GIT
Uses: Antispasmodic agent for Intestinal, biliary, renal colics as well as irritable bowel syndrome
Dosage: Oral as well as parenteral 40-80 mg TDS
ADRs: Headache, dizziness, flushing, Fall in BP
PDE 5 inhibitors:
- Enzyme located in corporal musculature
- Inhibit PDE V which is responsible for the breakdown of cGMP
- cGMP relaxes the smooth muscle and increases blood flow to the corpus cavernosum
- These drugs do not cause a chemical erection, Sexual stimulation is still needed to cause the initial release of nitric oxide, which stimulates the synthesis of cGMP
- Indicated in treatment of erectile dysfunction in men due to organic or psychological causes
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
- Doses: 25mg, 50mg, 100mg
- Most patients start at 50mg and it can be taken any time from 1/2 to 4 hours before sexual activity
- Max frequency is once per day
- Best to take it on an empty stomach
- Doses: 25mg, 50mg, 100mg
- Vardenafil (Levitra)
- Doses: 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg, and 20mg
- Most patients start at 10mg taken ~60minutes before sexual activity
- High fat meals can reduce the plasma concentration by 18-50% (on an empty stomach is not a bad idea)
- Doses: 2.5mg, 5mg, 10mg, and 20mg
- Tadalafil (Cialis)
- Doses: 5mg, 10mg, 20mg
- Most patients start on 10mg and it can be taken without regard to food
- Maximum dosing frequency is once per day
- Doses: 5mg, 10mg, 20mg
- Sildenafil (Viagra)
side effecs of the PDE 5 inhibitors,
all 3 of them have comman side effect of headache flushing nasal congestion and dyspepsia and the typical side effect related to the sildenafil is abnormal vision blue halos due to simultenous inhibition of pde 6 enzyme which is present in retina and typical side effect of vardanfil is flu syndrome and that of tadalafil is back pain,and myalgia which is unique for tadanafil .
Caution:
- Ability to potentiate NO – very cautiously used in patients of angina, HTN using nitrates
Interactions:
- Reduced activity in presence of enzyme inducers like rifampicin, carbamazepine etc.
- Increased activity in presence of enzyme inhibitors such as ketoconazole, cimetidine, erythromycin etc.
Off label use:
- PDE 5 also located in lungs, inhibition leads to raised cAMP leading to vasodilatation
- Used in pulmonary HTN
- Severe Raynaud’s Phenomenon associated with systemic sclerosis and digital ulceration.
- When given sildenafil for 4 weeks subjects had reduced mean frequency and duration of Raynauds attacks and a significantly lowered mean Raynaud’s condition score.
- The capillary blood flow velocity also increased in each individual patient and the mean capillary flow velocity of all patients increased significantly.
- Significantly improve neurovascular coupling without affecting overall cerebral blood flow by increasing brain levels of cGMP à Evoking neurogenesis and reducing neurological deficits in rats 2 or 24 hours after stroke àThis data suggest that PDE5 inhibitors may have a role in promoting recovery from stroke
PDE6 Inhibitors
- PDE5 and PDE6, being structurally related, compounds inhibiting PDE5 also interact with PDE6 .
- Zaprinast and dipyridamole inhibit PDE6 as potently as PDE5.
- Due to the adverse vision effects of PDE6 inhibitors and the specific localization of PDE6, in the retina
- There is no pharmaceutical investment on PDE6 inhibitors
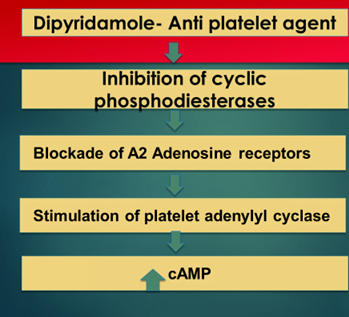
Dipyridamole is combined inhibitor of multiple PDE like 5,6,7,8,10,11 by inhibiting these enzymes it causes blockade of A2 receptor which stimulates platelet adenyl cyclase and in-turn cause increase in camp which is responsible for its antiplatelet effect
Papaverine
- Selective PDE 10 Inhibitor
- Opium alkaloid derived from poppy seeds
- Papaverine was discovered in 1848 by Georg Merck son of Emanuel Merck founder of the Merck corporation
- Use:
- Spasms of the gastrointestinal tract, bile ducts & ureter
- Cerebral and coronary vasodilator in subarachnoid hemorrhage (combined with balloon angioplasty and coronary artery bypass surgery)
- Smooth muscle relaxant in microsurgery where it is applied directly to blood vessels.
- PIPE therapy: papavarine /phentolamine induced penile erection therapy for rx of ED.
- Papavarine (3-20 mg) with or without phentolamine(0.5-1mg) injection used to produce penile erection in ED patients.
- disadvantages: skilled expert, Priapism 2-15 %, Penile fibrosis on repeated injections
