Endothelin and Endothelin Receptor Antagonists
Endothelin is a very potent vasoconstrictor peptide derived from the endothelial cells of vasculature.
Biosynthesis.
- ECE-1 is the rate-limiting step in ET-1 synthesis.
- ETs interact with two GPCRs, the ETA and ETB receptors
Endothelin Signaling.
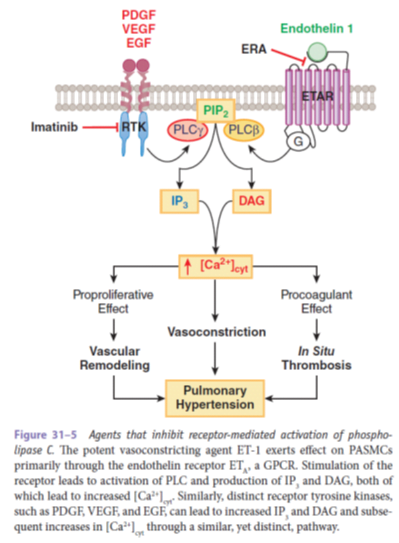
- Endothelin 1 à potent, endothelium-derived, constricting factor à mediated by the ETA receptor
●Nonselective dual action receptor antagonists – bosentan and macitentan
●Selective receptor antagonists of endothelin receptor A – ambrisentan and sitaxsentan
Sitaxsentan was withdrawn à several fatal cases of hepatoxicity
Ambrisentan is the least hepatotoxic of the ERAs
Commonalities.
- Common side effects of the classà headache, pulmonary edema, and nasal congestion/pharyngitis, with a risk of testicular atrophy and infertility.
- Bosentan and ambrisentan may increase liver transaminases, which should be monitored closely, and the drugs are contraindicated in patients with moderate-to-severe liver disease
- the elevation of liver enzymes generally resolves after discontinuation of treatment.
- metabolized by CYP3A4 and to some extent by CYPs 2C9 and 2C19.
- Inhibitors of these CYPs (e.g., ketoconazole and ritonoavir) can increase bosentan and macitentan exposure
- The ERAs are potent teratogens and should be used with caution in women of childbearing age.
- must not be used in pregnant patients.
- Documentation of a negative pregnancy test prior to initiation of therapy and a clear contraceptive plan are recommended, and fertile women must use two acceptable methods of birth control while taking ET antagonists.
Bosentan.
- orally effective, competitive antagonist of ETA and ETB receptors.
- In patients with PAH with mild to-severe functional impairment (functional classes II–IV)
- improves symptoms, functional capacity, and pulmonary hemodynamic parameters
- usually started at 62.5 mg twice daily, increasing to 125 mg twice daily after 4 weeks.
Macitentan.
- an orally active, competitive ETA and ETB receptor antagonist.
- At a dose of 10 mg daily, macitentan improves the time to disease progression or death in PAH and improves symptoms, functional capacity, and pulmonary hemodynamic measurements
- relatively well tolerated and has thus far not been associated with elevation of liver-associated enzymes, but caution is recommended.
Ambrisentan.
- Unlike bosentan and macitentan, ambrisentan is a relatively selective ETA antagonist (approximately 4000 times greater affinity for ETA than ETB).
- initiated at a dose of 5 mg daily and increased to a maximum of 10 mg daily.
- Liver-associated enzyme abnormalities are much less common than with bosentan, yet monitoring of liver function tests is still recommended.
Congestive heart failure (CHF)
CHF is a disease process characterised by impaired left ventricular function, increased peripheral and pulmonary vascular resistance, and sodium and water retention.
In patients with CHF, circulating ET-1 is elevated and correlates with symptoms20 and haemodynamic severity
Infusion of the mixed ETA/B antagonist, bosentan, has been shown to improve systemic and pulmonary haemodynamics in patients with CHF
Role of endothelin receptor antagonists in pulmonary arterial hypertension
Rationale for Antagonizing ET’s Effects in PAH.
- Endothelin 1 is implicated as a contributory factor in idiopathic PAH
- Plasma ET-1 levels are increased up to 10-fold in patients with PAH and
- correlate well with severity of disease and the elevation of right atrial pressure.
- There are no clinically available specific inhibitors of ECE-1, the rate-limiting step in ET-1 synthesis, but a number of orally effective small molecule antagonists of ET receptors have been developed.
- Despite the opposing effects of ETA and ETB receptor activation, pharmacological targeting of specific ETA receptors has not led to significantly altered clinical responses compared to dual antagonism (e.g., antagonism of ET-1 binding to both ETA and ETB receptors) in treating PAH.
High concentrations of ET-1 have been recorded in the lungs of patients with PAH
Bosentan, an orally active non-selective endothelin receptor antagonist, has been proved to be effective in the treatment of pulmonary arterial hypertension (PAH)
