Recent advances Diabetes Mellitus
Why need newer drugs?
Limitations of existing drugs:
Insulins: Repeated injections, Lipodystrophy, insulin resistance, cannot mimic the physiological nature of insulin release
OHAs: Adverse effect profile-unacceptable: weight gain; abdominal distention and flatulence with acarbose
Basic pathology is left unaltered, no strategy available to protect beta cells
Type I DM
- Insulin Degludec (sept 2015)
Degludec is injected subcutaneously:
- forms multihexameric complexes that slow absorption;
- binds to albumin
these two characteristics contribute to the prolonged effect of Degludec (>24 h at steady state).
- Common adverse reactions (excluding hypoglycaemia) reported with insulin Degludec included nasopharyngitis, upper respiratory tract infection, headache, sinusitis, diarrhoea, and gastroenteritis. Hypersensitivity, lipodystrophy, injection-site reactions, weight gain, and peripheral oedema were also reported
- Inhaled insulin
- Inhaled insulin (Afrezza) (June 2014) is formulated for inhalation using a manufacturer-specific device.
- In combination with a long-acting
- More rapid onset and shorter duration than injected insulin analogues
- Adverse events include cough and throat irritation
- It should not be used in individuals who smoke and those who quit smoking less than 6 months ago
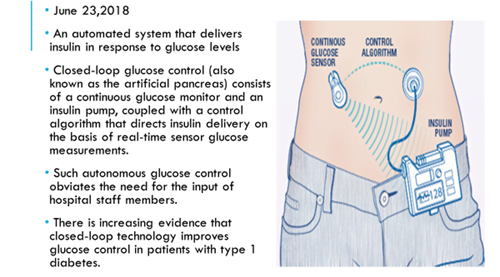
- Artificial Pancreas

- Gad vaccine
- Autoantigen GAD (glutamic acid decarboxylase)-vaccine is safe for children at high risk for developing type 1 diabetes
- The drug is given before onset of type 1 diabetes.
- Phase 2b
- Results by 2020
Type II DM
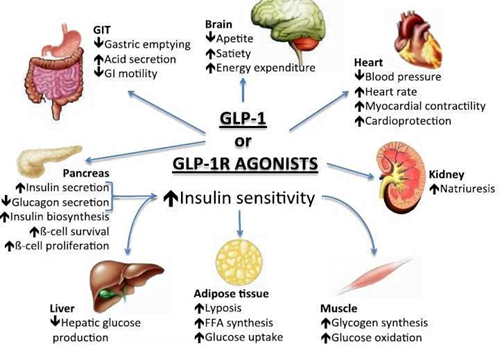
- GLP1 receptor agonists
- GLP-1 is a naturally occurring hormone responsible for the incretin effect.
- The insulinotropic effect of GLP-1 is glucose dependent in that insulin secretion at fasting glucose concentrations, even with high levels of circulating GLP-1, is minimal
- Insulin secretion occurs in 2 phases.
- 1st phase – immediate rise in insulin after meal lasting approximately 10 minutes.
- 2nd phase – insulin is released more slowly for a prolonged period.
- T2DM – markedly reduced first phase insulin secretion & ↑ second phase
- Prolonged elevation of insulin from persistent hyperglycaemia leads to beta cell toxicity and ultimately contributes to insulin resistance.
- Interventions that mimic normal first phase insulin secretion, rather than the second phase, have been correlated with improved glucose tolerance.
- Albiglutide Weekly (apr 2014)
- Dulaglutide Weekly (sept 2014)
- Exenatide Weekly (2011)
- Liraglutide Daily (jan 2010)
- Lixisenatide Daily (July 2016)
- Semaglutide once weekly (Dec 2017)
Semaglutide
specifically indicated as an adjunct to diet and exercise to improve glycemic control in adults with type 2 diabetes mellitus.
contraindicated in patients with a personal or family history of MTC or in patients with Multiple Endocrine Neoplasia syndrome type 2 (MEN 2).
ITCA-650
- FDA has accepted NDA filing for the drug ITCA 650 (continuous subcutaneous delivery of exenatide) in 2017.
- The drug therapy is designed to utilize a subcutaneous osmotic mini-pump for continuous delivery of exenatide drug for a period of one year.
- The FREEDOM clinical trial program conducted for ITCA 650 demonstrated highest HbA1c reductions in patients receiving combination dose of metformin.
- ITCA 650 is the first once/twice yearly, injection-free GLP-1 therapy available globally
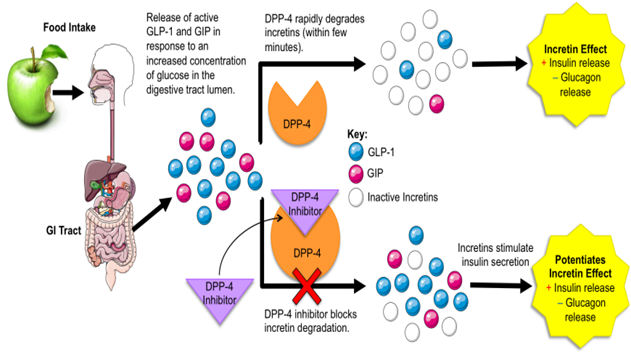
- DPP4 inhibitors
- GLP1 is degraded by dipeptidyl peptidase (DPP)4, resulting in a shorter half life
- This has led to the development of DPP4 inhibitors, which inhibit the degradation of GLP 1
- Alogliptin 25 Daily (jan 2013)
- Linagliptin 5 Daily (may 2011)
- Saxagliptin 2.5–5 Daily (July 2009)
- Sitagliptin 25–100 12–16
- Vildagliptin 50–100 Twice daily Europe 2007
- The FDA has issued a warning that this class of drugs is rarely associated with severe joint pain.
- Patients treated with saxagliptin had an increase in hospitalization for heart failure
- Na+-Glucose Transporter 2 Inhibitors
- SGLT2 is a Na+-glucose cotransporter located almost exclusively in the proximal portion of the renal tubule
- SGLT2 accounts for 80%–90% of glucose reclamation
- Canagliflozin (Apr 2013)
- dapagliflozin (Jan 2014)
- Empagliflozin (Aug 2014)
- Ertugliflozin (Dec 2017)
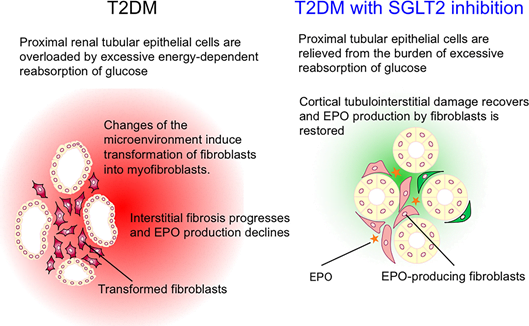
- SGLT2 inhibitors reduce the burden on the proximal renal tubules.
- SGLT2 inhibitors reduce central sympathetic overactivity, probably by suppressing renal afferent signaling to the brain.
- A mild state of ketosis also contributes to reduction of sympathetic tone.
- Decreased sympathetic outflow from the brain to the kidney alters the pressure–natriuresis relationship so that the kidneys excrete more sodium and water at a given pressure, thereby improving fluid retention.
- It may also suppress the renal renin–angiotensin system (RAS) and augment circulating natriuretic peptide levels by attenuating renal neprilysin activity, thereby correcting the imbalance between the natriuretic peptide/soluble guanylate cyclase (sGC)/cyclic guanosine monophosphate (cGMP) pathway and the RAS pathway, leading to cardiovascular and renal protection.
Adverse events
- There is a small (1%–2%) increase in lower urinary tract infections and a 3%–5% increase in genital mycotic infections (FDA warning)
- Urine glucose losses cause mild diuresis, which can lead to hypotension
- Potency decreases by 40%–80% across the spectrum of stage 3 kidney disease
- Increase the risk of fractures (FDA warning), affect mineral balance and circulating levels of parathyroid hormone and 1,25-hydroxy vitamin D
- Diabetic ketoacidosis
- Canagliflozin is associated with an increased risk of lower extremity amputation.
Recently Approved FDC – type II DM
- Sitagliptin + Simvastatin 2011
- Linagliptin + Metformin 2012
- Dapagliflozin + Metformin 2014
- Empagliflozin + Metformin 2015
- Insulin degludec + Liraglutide 2016
- Insulin glargine + lixisenatide 2016
- Dapagliflozin +Saxagliptin 2017
Drugs in pipeline
- Sotagliflozin –
- oral inhibitor of sodium–glucose cotransporters 1 and 2 (SGLT1 and SGLT2)
- SGLT1 inhibition reduces glucose absorption in the proximal intestine
- SGLT2 inhibition decreases renal glucose reabsorption.
- Dual PPAR alpha/gamma agonist à Saroglitazar
- first in class drug – dual PPAR agonist at the subtypes α (alpha) and γ (gamma) of the peroxisome proliferator-activated receptor (PPAR).
- Agonist action at PPARα lowers high blood triglycerides,
- Agonist action on PPARγ improves insulin resistance and consequently lowers blood sugar.
- The results of phase 3 clinical trials indicate that saroglitazar is devoid of conventional side effects of fibrates and pioglitazone
- Approved in India 2013 for diabetic dyslipidemia and hypertriglyceridemia in T2DM not controlled by statin therapy
- Phase II US – for NASH in 2016
Human Embryonic Stem Cells (HESCs)
- Stem cells can provide a non-exhausting source of the degenerated β cells in T2D patients – cultivated & transplanted
- Researchers are trying to develop and establish functional β cell mass from different types of somatic stem cells, which can prove to be a miraculous therapy.
- Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) [bone marrow, adipose tissue, umbilical cord or its blood, fibroblasts and liver cells] – glucose induced insulin-secreting cells, arrest insulin resistance, recovery of liver and pancreas damage and to cure diabetic ulcers and limb ischemia.
- MSCs transplantation also leads to elevation of GLUT4, insulin receptor substrate 1 (IRS-1) and Akt (protein kinase B).
- Limitations of the use of stem cells are the ethical issues involved. Safety issues involved must be considered prior to clinical application.
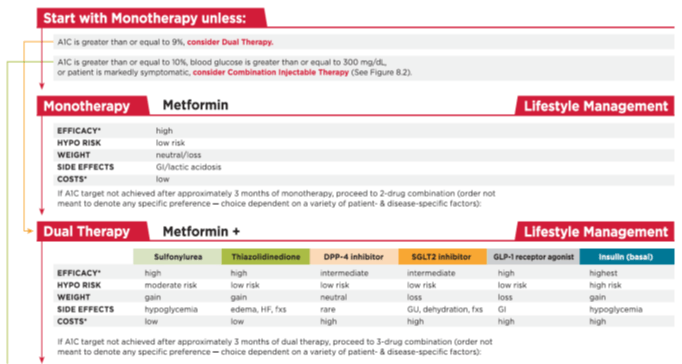
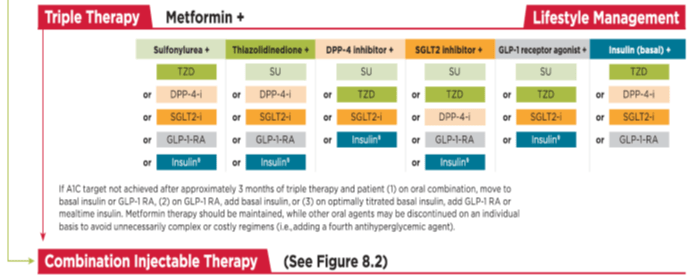
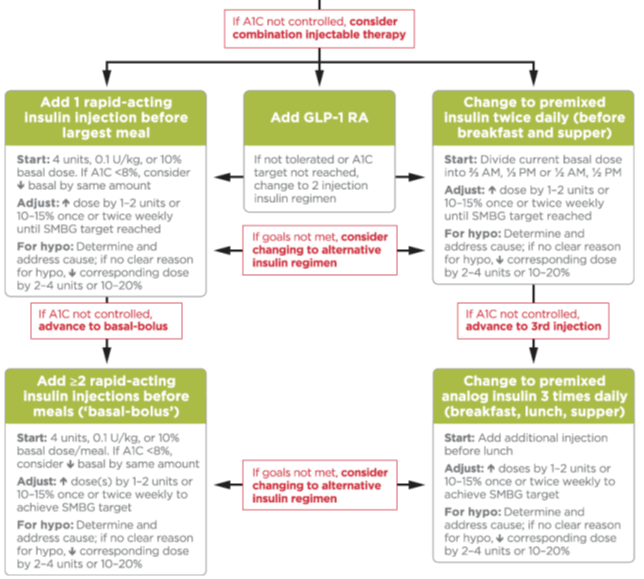
American Diabetes Association 2017 guidelines: