Insulin Analogues
Molecules produced by genetic engineering wherein the amino acid sequence in human insulin is changed to alter its pharmacokinetics.
However, they bind to insulin receptors in the same way as human insulin and produce similar effects
Also termed as Designer Insulins, Insulin receptor ligands, Democratic insulins
Novel short or long acting insulin analogues also called ‘designer insulin’.
- discovered by Banting and Best in 1921. It consists of 51 amino acids
- Pork insulin differs from human insulin by one amino acid only whereas
- beef insulin has a difference of three amino acids.
- Addition of zinc makes it long acting.
- Half-life of insulin in plasma is about 5-6 minutes.
- Glucose is the main stimulus for the release of insulin from the β cells of pancreas.
- Glucose stimulates GLUT-2 and inhibits ATP sensitive K+ channels; factors that are responsible for the depolarization of β cells and release of insulin.
- α2 receptor stimulation inhibits insulin secretion whereas β2 agonists and vagal stimulation enhances insulin release.
Actions
1. It decreases blood glucose by
• Stimulating the entry of glucose in muscle and fat (by increasing the synthesis of GLUT 4).
• Inhibiting glycogenolysis (by inhibiting phosphorylase) and gluconeogenesis (by inhibiting phosphoenol pyruvate carboxykinase). These processes are inhibited at lower concentration of insulin.
• Increasing glycolysis (by stimulation of glucokinase) and glycogenesis (by stimulating glycogen synthase). These require more concentration of insulin.
2. It inhibits lipolysis and thus favors triglyceride deposition.
3. It increases the synthesis and inhibits the breakdown of proteins.
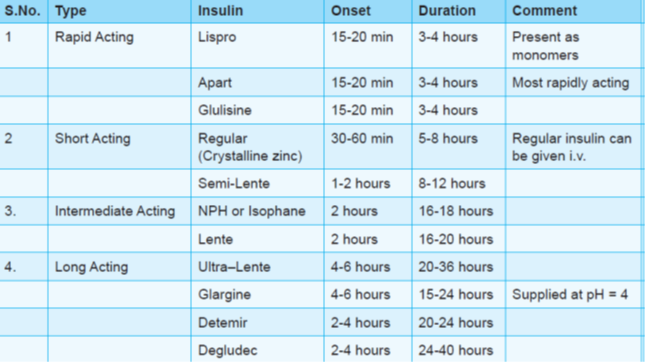
Human insulin (humulin) is prepared by recombinant DNA technology and has rapid absorption (from s.c. route) and shorter duration of action. Recently ultrashort acting (insulin lispro, glulisine and aspart) and ultralong acting (insulin detemir and glargine) preparations have also been developed.
What was the need for insulin analogues when we had improved insulins???

Insulin analogues were developed to overcome the limitations of
available insulins:-
– Ultrashort acting analogues to overcome limitations of short acting insulins(regular)
– Long acting analogues to overcome limitations of long/intermediate acting insulins(NPH)
ADVANTAGES OF GLARGINE OVER NPH
Low insulin levels maintained uniformly for 24hrs with no peak(mimics physiological basal insulin secretion)
– Decreased risk of nocturnal hypoglycemia
– Fasting & interdigestive blood glucose levels effectively controlled throughout the day irrespective of the time of injection
– Suitable for once daily dosing.
– Predictable absorption independent of dose/site of inj/exercise/mixing
All insulin preparations are supplied at neutral pH (7.2.-7.4) except glargine (supplied at pH 4.0). Therefore, glargine cannot be mixed with any insulin.
• All insulin preparations contain buffer (phosphate or acetate) except regular, glulisine and glargine.
• If regular insulin is mixed with lente or ultralente insulin, it can loose its rapidity of action.
Insulin Degludec : Newest long acting basal insulin with longer half life (25-40 hr). Can be given any time of the day or thrice weekly. Unlike glargine, it is effective at physiological pH.
Route of administration
• All preparations can be given by s.c. route.
• Only regular (crystalline zinc) insulin can be given i.v.
• Inhalational insulin (exubera) had lead to lung cancers and fibrosis.
In june 2014, a new inhalational insulin (Afrezza) was approved by FDA for type-1 DM. It should not be used in patients with chronic lung diseases like asthma.
Continuous subcutaneous insulin infusion (CSII) through pumps
-Most physiological method of insulin delivery
-Preferred in patients uncontrolled on multiple injections & those needing excellent control(pregnancy)
-Specially suitable for patients with risk of hypoglycemia, uncertain lifestyles, meal times.
- Consists of insulin reservoir, program chip, keypad & screen.
- Insulin infused through plastic tubings connected to s/c inserted infusion set .
INSULIN DELIVERY – short acting insulin analogues like Aspart > lispro used.
- Provides constant basal infusion of insulin & patient can activate pre-meal boluses.
- Pumps can be discontinued for short periods for activities like exercise
- Pump can be pre-programmed to compensate for nocturnal & early morning glucose fluctuation.
- Advantages
- Rate of insulin absorption more predictable than multiple injections
- Risk of hypoglycemia less
- Drawbacks
- Pump failure àketoacidosis
- Injection site abscess
- Only motivated & committed patients can use it.
Insulin pens (ultra-short acting/long acting/pre-mix analogues)
Inhaled Insulin
• By pulmonary route drugs have faster onset of action, even faster than i.v. route and large surface area of lungs causes more systemic absorption.
• Exubera is first inhalational drug to be approved by FDA on Jan 2006.
• Bioavailability is just 10% compared to regular human insulin given by subcutaneous route with duration of action of 5-10 hours.
• Therefore, high doses of insulin have to be given about 8 times the subcutaneous route to achieve glycemic control.
The major problems are loss of drug with inhaler and mouth during inhalation, variation in absorption due to age related difference, respiratory tract infection and smoking.
• Other side effects are mild to moderate cough, shortness of breath, sore throat and dry mouth.
Discontinued later due to lung complications and inconvenient use reported by users.
Afrezza
ultarapid acting insulin which is inhaled at beginning of a meal & was approved in 2014 by the FDA. administered via a whistle-sized inhaler called the ‘Dreamboat’.
Afrezza peaks within 12 -15 minutes and is out of the system within an hour.
The Dreamboat is meant to be thrown away after 15 days to prevent any powder buildup inside that could clog the device.
Unlike traditional insulin, it needs no refrigeration, but rather is kept at room temperature.
Each single-use cartridge holds either 4 or 8 units.
Not recommended for people with diabetes who smoke, nor for treating diabetic ketoacidosis (DKA).
Can cause bronchospams in asthma/COPD patients.
Hypoglycemia, cough, and throat pain or irritation are the common side effects reported in CTs.
Long term PMS studies are underway
Orally absorbed insulin(oralin)
Generex has developing an aerosol containing insulin for buccal absorption , using an applicator similar to those used in asthma medications.
Transdermal insulins
• Altea has developed trandermal patches for insulin delivery.
• The electronic adhesive patch is first applied to the skin , vaporizing superficial dermal cells and forming micropores for insulin to pass through, and then insulin patch is applied.
• It provide basal insulin delivery for 12 hrs.
Newer Advances
LY2605541 is a PEGylated basal insulin lispro.
Has completed Phase II clinical trials.
insulin molecule is embedded in a polyethylene glycol (PEG) chain.
The resultant molecule is quite large and absorption from the subcutaneous space is slowed significantly, prolonging the duration of action.
Comparable or better glycaemic control than insulin glargine as well as reduced weight in patients with T1DM and T2DM.
Factors affecting insulin absorption
• Site of injection (most rapid from abdomen followed by arm, buttock and thigh).
• Type of insulin (Fast with regular, aspart, lispro and glulisine)
• Subcutaneous blood flow (rate increases with massage, hot bath or exercise).
• Depth of injection (faster with i.m. than with s.c. route)
Complications of insulin therapy
• Most common complicationà hypoglycemia that can be treated by glucose (oral or i.v.) or glucagon (i.v.).
• Lipodystrophy at the injection site can occur with conventional preparations and the chances are less with highly purified and recombinant forms of insulin.
• Allergic reactions like lipoatrophy can occur with conventional preparations.
• Sodium and water retention leading to edema has been rarely reported.
Drug interactions
• Use of non-selective beta blockers in patient on insulin therapy delays the recovery from hypoglycemia (less chances with cardioselective beta blockers). These drugs may also mask the warning signs of hypoglycemia i.e. palpitations, tremors and anxiety.
All the warning signs may be masked except sweating (It is mediated by sympathetic cholinergic fibres and not by beta receptors)
• Acute consumption of alcohol can precipitate hypoglycemia.
• Drugs elevating blood glucose (diuretics, corticosteroids, oral contraceptives and diazoxide etc.) decrease the effectiveness of insulin.
Indications of insulin therapy
• All cases of IDDM
• NIDDM patients
–– Not controlled on OHA
–– In pregnancy
–– In complications like diabetic ketoacidosis and hyperosmolar coma (regular insulin i.v. is preferred).
–– To tide over stressful conditions like infections and surgery etc.
• Acute hyperkalemia
