Alternatives to animal experiments
Zebra fish (embryology studies), C elegans, Drosophila (Parkinson), pond snail.
- Animal models are used to test possibilities that would be difficult or impossible to test using the target species (Humans)
- It is mandatory to do extensive toxicological studies in animals before the candidate drug gets approval for clinical trials in humans
- Animals are used in science for:
- Undergraduates teaching to learn physiological mechanism, anatomy and effect of various drugs on human body
- Postgraduate teaching to show effects of various drugs, to find out the nature of unknown drug and for bioassay
- Research to conduct screening for drugs, bioassay and for preclinical testing of new drug
Need for alternatives
- In the laboratory an animal maybe
- Poisoned, Deprived of food, water and sleep
- Applied with skin and eye irritants
- Subjected to psychological stress, Deliberately infected with disease
- Brain damaged, Paralysed, Surgically mutilated
- Force fed and electrocuted for experiment
- Disadvantages of animal experiments
- Pain, distress and unethical behaviour to animals
- Requirement of skilled manpower, time consuming protocols
- Translation rates of animal experiments are abysmal
Alternatives to animal experiments
- Continued but modified use of animals
- In vitro (test tube) test methods and models based on human cell and tissue cultures
- Computerized patient-drug databases and virtual drug trials
- Computer models and simulations
- Computer assisted learning
- Non-invasive imaging techniques such as MRIs and CT Scans
- Micro-dosing.
- Continued but modified use of animals
- Russel and burch in 1959 proposed that “if animals were to be used in experiments, every effort should be made to replace them with non‑sentient alternatives”
- They developed the 3R strategy which includes
- Refinement– refine experimental methods to decrease unnecessary pain and trauma to animals
- Setting the earliest possible end point
- Using appropriate analgesics and anaesthetics for painful procedure
- Use proper handling technique for animals
- Adequate training prior to performing experiment
- Ensure drug doses are correct and drugs are not expired
- Perform surgeries and procedure aseptically to prevent infection,
- Refinement– refine experimental methods to decrease unnecessary pain and trauma to animals
- Reduction– reduce the number of animals used in these experiments
Perform pilot studies- Design studies to use animals as their own controls eg- Cross over study
- Gather data for more than one experiment concurrently
- Consult with statistician and use minimum number of animals
- Minimise variables such as disease, diet, stress, genetics
- Use appropriate species of animals
4R, 5R –rehabilitate, reuse
- Replacement– replace the animal experiments eg- computer simulation models, In-vitro methods, cell culture techniques
- Substitution of insentient material in place of conscious higher animals
- Could be relative or absolute
- Replace higher animals with lower animals
- Replace live animals with dummies for teaching and dissection purpose
- Use computer simulation and in vitro methods
- Use cell culture and tissue culture
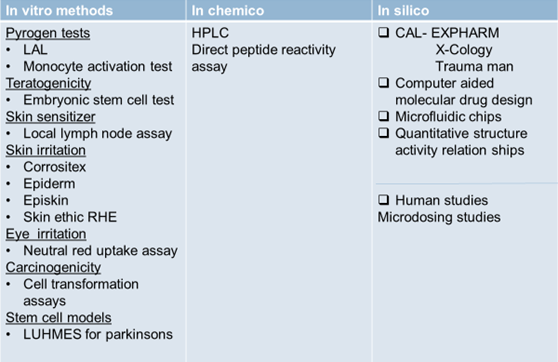
In vitro methods
- In vitro Pyrogen test
- Rabbit pyrogen test is replaced with
- Limulus amoebocyte lysate(LAL)
- Principle-Lipopolysaccharides cause extracellular coagulation of blood( Haemolymph) of horseshoe crab Lumulus Polyphemus
- Three techniques to perform this test
- Gel clot technique- based on gel formation
- Turbidimetric method-based on development of turbidity after cleavage of endogenous substrate
- Chromogenic method-based on development of color after cleavage of synthetic peptide chromogen complex
- Limulus amoebocyte lysate(LAL)
- Rabbit pyrogen test is replaced with
Disadvantage-
- Overestimate the pyrogen content of other products
- Does not detect pyrogens other than bacterial endotoxins, viruses and fungi
- Monocyte activation test Uses human mononuclear cells obtained from human volunteers or from blood bank Very specific and sensitive Detects pro-inflammatory contaminants Better than LAL and rabbit pyrogen test
- Based on the response of human leukocytes which release inflammatory mediators in response to pyrogen contamination
- Embryonic stem cell test
- Used for detection of any embryonic toxicity
- Principle- the capacity of stem cells(rodent cell line D3) to develop into specialized contracting heart cells in vitro within 10 days is assessed using light microscopic evaluation
- End points –
- Inhibition of differentiation
- Cytotoxic effect on the ES cells
- Cytotoxic effect on 3T3 fibroblasts
- Positive result classifies the chemical as likely to be hazardous for development and reproduction
- Better alternative to study cancer, liver and cardiac toxicity
- Local lymph node assay for skin sensitization
- Used to test the potential of test compound for skin sensitization
- Principle- a test compound is considered as a sensitizer when the lymph node draining the site of chemical application reveals a primary proliferation of lymphocytes as measured by radioactive labelling in test and vehicle groups
- Proliferation is proportional to dose applied
- Stimulation index- ratio of proliferation in test groups to that of control
- Index must be atleast 3
- Clinical skin patch test on human volunteers
- Corrositex
- To determine chemical corrosivity.
- Replaces rabbit test of dermal corrosivity
- Principle- a unique bio membrane and chemical detection system which becomes colored when exposed to potentially corrosive substance
- Cultured human epidermal keratinocytes mimic human epidermis are used to measure skin irritation and dermal corrosion.
- Replaced the Draize rabbit skin irritation test
- Corrositex
- Neutral red uptake assay
- Alternative to Draize rabbit eye test for screening of chemicals for eye irritation potential
- Neutral red penetrates cell membrane and accumulates intracellularly in lysosomes
- Alteration of cell surface or lysosomal membrane result in decreased uptake
- NRU assay measures the ability of test compound to inhibit uptake of neutral red dye
- NRU 50 or IC 50 serves as toxicological end point
- Carcinogenicity test
- By using cell transformation assays
- Eg-1. Balb/c3T3 assay
- 2. Syrian hamster embryo (SHE)
- These assays are faster, less expensive, and involve fewer animals
- Alternative to rodent bioassay and transgenic mouse model bioassay for carcinogenicity assays
- 8 animals against 800 or more in a standard bioassay
Stem cell models
A human neuronal model cell line called LUHMES in which tyrosine kinase activity has been augmented to make these cells as similar as possible to human brain cells in-vivo
- Can be used for toxicological screening and also as invitro models of disease
- Disease genes are inserted into embryonic stem cells, induced to differentiate into human disease tissue which is used for screening of drugs
- Eg- Genes from a Parkinsons patient were introduced in embryonic stem cells which grew into a model of Parkinsons disease and is used for screening potential drugs
- Alzheimers and Diabetes models
- Repeated dose toxicity test
- Computerized biokinetic modeling is used as a means of predicting the distribution of chemical among various organs and tissues of the body and also to predict organ specific toxicity
- Such predictions are verified quantitatively using cell cultures of specialized tissues
Microorganism based model
- Tetrahymena pyriformis—a ciliate protozoan being used to study the effects of anesthetics on metabolism
- Salmonella typhimurium—bacteria used in mechanistic studies in genetics as well as the Ames mutagenicity/carcinogenicity test
IN CHEMICO TESTING
- The toxic potential of substances can sometimes be detected using relatively simple chemistry based methods and not requiring human cells.
Eg- High performance liquid chromatography - Direct peptide reactivity assay– used to assess whether a chemical or cosmetic will cause allergy
- The tests works by mimicking a key step in the development of allergies – the binding of proteins found in the skin to the substance.
- If proteins bind to the substance then it is very unlikely that it will cause an allergic reaction
IN SILICO MODELS
- Computer aided molecular drug design
- Quantitative structure activity relationships
- Computer assisted learning
- CAL deals with a range of software packages which simulate the animal experiments
- Two software’s are currently used in India
- Expharm– developed by JIPMER, India
Contains programs on
- Effect of drugs on the rabbit eye
- Bio assay of histamine using guinea pig ileum
- Effect of drugs on the frog heart
- Effect of drugs on dog blood pressure and heart rate
- Effect of drugs on the ciliary movement of frog esophagus
- The user can conduct experiment and collect data
- Each program can be run in two modes-
a) tutorial mode, (b) examination mode
- X-cology video demonstrations of different procedures like isolation and mounting of animal tissues Screen interactive interface to study the effects of various drugs on the isolated tissuesContent is classified into three sectionsExperimental animals Equipment Experimental technique – procedure to carry out bioassay and experiments on whole animals
- Computer or mathematical analysis
- Translation of biological effect into a mathematical equation.
- Virtual human organs and virtual metabolism programmes can now predict drug effects in humans more accurately then animals can.
- Computers design the molecular structure of drugs to target specific receptors
- Eg- Protease inhibitors were designed by computers and tested in tissue culture and computer models bypassing animal tests
- Microfluidic chips
- Chips 2 cm wide and contain a series of tiny chambers each containing a sample of tissue from different parts of the body.
- The compartments are linked by microchannels through which a blood substitute flows
- The test drug is added to the blood substitute and circulates around the device
- Sensors in the chip feedback information for computer analysis
- This can be used to study the disease process and drug metabolism
- Micro-dosing
- A ‘microdose’ is defined as less than one hundredth of the proposed pharmacological dose up to a maximum of 100 µg
- Can be measured in any biological sample including plasma and urine to determine ADME
- Analysed using an accelerator mass spectrometer (AMS).
- Early metabolism data can be obtained before going into human phase 1 trials.
- Allows testing in relevant species
