Eval of antianginals:
- Limitations of present drugs:
- Affect hemodynamic parameters.
- Do not protect the heart against stress induced adrenergic effects.
- Tolerance develops.
- Beneficial effects are short-lived.
In-vitro methods:
- Isolated heart (Langendorff) technique
- Isolated heart-lung preparation
- Calcium antagonism in isolated rabbit aorta
- Relaxation of bovine coronary artery
- Coronary artery ligation in isolated rat heart
- Plastic casts from coronary vasculature in dogs
Isolated heart (Langendorff) preparation
- Principle: heart is perfused in a retrograde direction from aorta which closes aortic valves. So the perfusate enters coronary circulation.
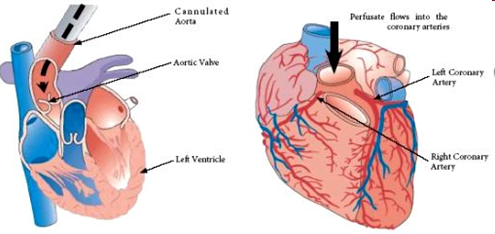
- Procedure for excision of heart à Anaesthesia à Heart is excised along with aorta à Cannulation of aorta à Perfusion fluid à Assessment of contractile function
Indices measured
- Morphology of heart
- Biochemistry
- Cardiac rhythm and electrophysiology
- Contractile function of heart
- Coronary flow
- Pharmacology
- Arrhythmias
- K+ levels
- Calcium antagonism
- EDRF release from coronary bed
- Electrophysiological evaluation of CV agents
Advantages
- Highly reproducible, low cost and large numbers can be studied
- Broad spectrum parameters can be measured
- Absence of confounding factors (neurohormonal)
- Allows induction of regional or global ischemia
- Hypoxia can be imposed
- Ischemia-reperfusion and arrhythmia studies
Disadvantage
- Constantly deteriorating preparation
Isolated heart-lung preparation
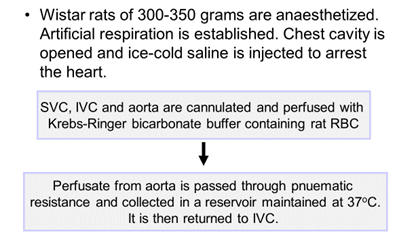
Isolated rabbit aorta:
Rabbit sacrificed à
Abdominal aorta isolated, cut into small rings and mounted in tissue bath containing Krebs buffer à
Addition of Kcl or NE induces contraction in the aortic rings.

Relaxation of bovine arteries:
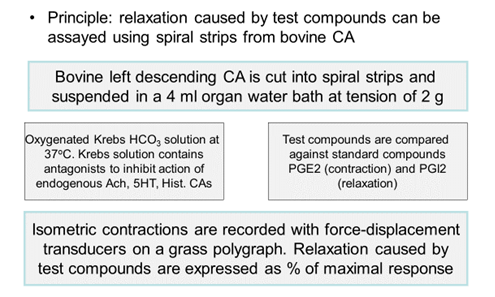
- Coronary artery ligation:
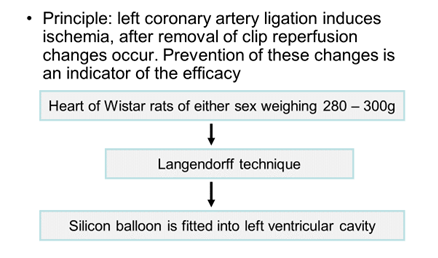

- Plastic casts:
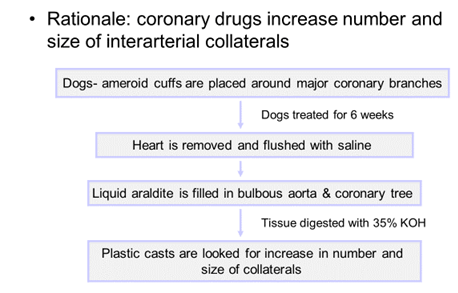
- In-vivo methods:
- Occlusion of coronary artery
- Microspheres-induced acute ischemia
- Isoproterenol-induced myocardial necrosis
- Stenosis-induced coronary thrombosis model
- Electrical stimulation-induced coronary thrombosis
- Myocardial ischemic preconditioning model
- Occlusion of coronary artery in dogs:

Using Barium sulphate coronary arteriograms are made and infarcted area measured using X ray.
P-Nitro blue tetrazolium is used to visualize infarcted area. These are compared between test and control.
- Microsphere induced acute ischemia:
- Dog anesthetized.
- Micro-spheres are injected into the LCA to induce ischemia.
- Test/control administered.
- Parameters measured: Systolic and Diastolic pressure, LVEDP, HR, Pulmonary capillary pressure, PAP, COP between test and control.
- Isoproterenol induced Myocardial necrosis:
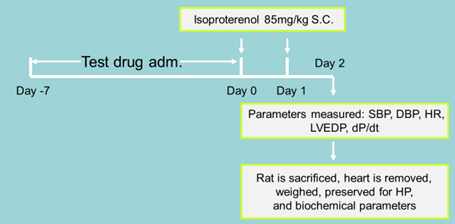
- Parameters measured: Systolic and Diastolic pressure, LVEDP, HR, Pulmonary capillary pressure, PAP, COP and compared between test and control.

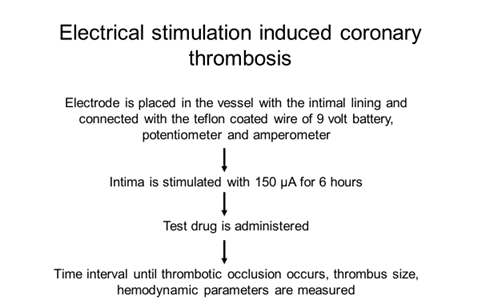
Ischemic preconditioning model:
- Rationale is that preconditioning decreases the damage caused by ischemia-reperfusion injury and this model tests those drugs that help in up-regulating the ischemic preconditioning.
- Rabbit are anesthetized.
- The LCA is ligated for 5 min and then released for 10 min.
- Test/control or vehicle is administered.
- This is f/b again ligating the LCA for 30 minutes and then re-perfusing.
- The hemodynamic parameters are compared b/w test and control.
Measurement of coronary blood flow:
- Electromagnetic flowmeter
- Inert gas technique
- Radioactive technique
- Radioactive microsphere technique
- Thermodilution technique
- Coronary arteriography
- Electromagnetic flow-meter: Two opposite magnetic poles are placed on either side of a coronary vessel. Distally two chromium-vanadium electrodes are placed adhering to the coronary vessel. The magnetic field perpendicular to blood flow generates a voltage which is picked up by electrodes and recorded.
- Clinical evaluation:
- Criteria (Parameters) of efficacy:
- Exercise capacity (total exercise time, maximum MET[metabolic equivalent of task] level achieved, maximum workload achieved, maximum heart rate and the double product.)
- ECG characters: Time to onset of angina, time to ST depression (by 1 mm), magnitude of ST, time taken for normalization after ST depression, exercise induced ventricular arrhythmias
- Coronary diameter
- Frequency of anginal pain/need to consume short acting nitrates
- HRQOL
- Morbidity and mortality (since the target of anti-anginal therapy is essentially symptoms control, at present, there is no requirement to prove beneficial effect on these variables in terms of efficacy)
- Phase 1:
- Subjects:
- Patients with stable angina pectoris for preceding 4 weeks without any change.
- Patients with stable angina, 6 months after revascularization
- Patients with stable angina 30 days after MI
- Stable means last <20 minutes and relieved immediately by rest.
- Parameters:
- Pharmacodynamic: hemodynamic effects at rest and during exercise (can be documented by MRI or myocardial perfusion imaging). EXERCISE PARAMETERS, EFFECT ON RENAL FUNCTION, PULMONARY FUNCTION, PLAETLET FUNCTION, GLUCOSE AND LIPID METAB.
- PK: Cmax, Tmax, t1/2, AUC
- Interactions: Pharmacokinetic and pharmacodynamic interactions should be investigated primarily with other frequently coadministered drugs in the target population.
- Phase 2:
- Subjects: Same as phase 1
- Parameters: CRITERIA FOR EFFICACY EXPLAINED ABOVE
- Design: randomized, placebo-controlled and double-blinded
- Wash-out: Withdrawal of ongoing anti-anginal meds
- Placebo run-in: 2 weeks atleast. Short acting nitrates for exacerbations are allowed in this period.
- Dosing interval: atleast 6 weeks to establish clinically useful dose range. Atleast 3 doses should be used.
- Phase 3:
- Subjects: Same as phase 1
- Parameters: CRITERIA FOR EFFICACY EXPLAINED ABOVE
- Design: randomized, active-controlled and double-blinded. Dose from phase 2 should be chosen. Should be of atleast 12 weeks.
- Studies where the new drug is administered as both monotherapy and add-on therapy should be carried out.
