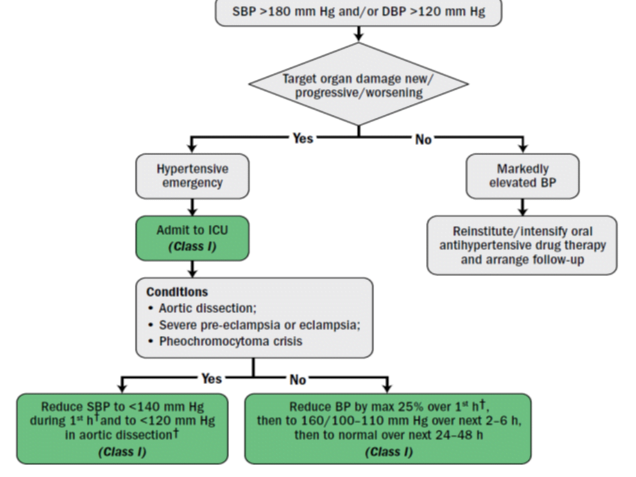
Hypertensive Crisis
systolic blood pressure (SBP) level ≥180 mmHg and/or a diastolic blood pressure (DBP) level ≥ 120 mmHg with or without acute target organ damage (TOD).
Hypertensive Urgency
- It is defined as elevation BP greater than 180/120 mm Hg, without signs of Target Organ Damage (TOD).
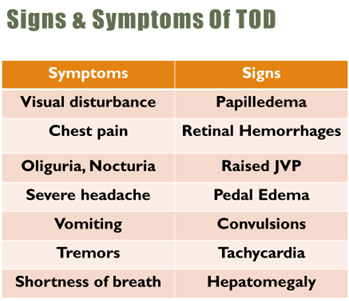
- Presenting symptoms include headache, shortness of breath, anxiety, and epistaxis.
Hypertensive Emergency
- It is defined as elevation of BP greater than 180/120 mm Hg in presence of signs of TOD
- Global burden – 24% & 21% of male & females with HTN (SBP>=140 OR DBP>=90).
India – Prevalence of HTN is 25% in urban & 10% in rural people in India of which 20.6% are men & 20.9% women.
Causes
- Non-adherence to anti-hypertensive medication
- Renovascular Disease
- Pheochromocytoma
- Hyperaldosteronism
- Drug Induced hypertension
- Eclampsia/pre-eclampsia
- Vasculitis
Diagnosis
- History – Hypertension, Medications, Substance abuse, Comorbid conditions
- BP – Both arms, Supine & Standing (Aortic dissection)
- Cardiac – ECG, Cardiac Enzymes, 2D-echo, X-ray
- Renal – Serum Creatinine & BUN, Liver Enzymes
Management
- Not addressed in recent JNC-8
- Current recommendations based on
- JNC-7 guidelines
- ACC/AHA 2017
Normalisation of BP is usually not recommended
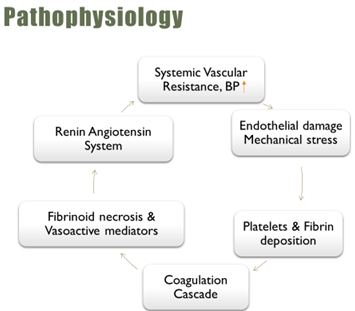
- Sudden fall in BP may cause acute hypoperfusion of vital organs & results in myocardial ischemia, hemiplegia, or acute renal failure.
Hypertensive Urgency
- Remember: Start Low, Go Slow
- Fully titrate before adding second med
- Titrate to effect (or side effect)
- Treatment with an oral, short-acting agent such as Captopril, Labetalol
- Increasing dose, Use of combination
Goal of Therapy: Hypertensive Emergency
- <1hr à Reduce Systolic Blood Pressure(SBP) ≤ 25%
- 2-6hr à if stable, reduce to 160/100–110 mmHg
- 24-48hr à Well tolerated & stable toward normal BP
Pharmacotherapy
- Vasodilators
- Sodium nitroprusside
- Nitro-glycerine
- Nifedipine
- Nicardipine
- Clevidipine
- Fenoldopam
- Hydralazine
- Enalaprilat
- Adrenergic inhibitors
- Labetalol
- Esmolol
- Phentolamine
Sodium Nitroprusside – MOA – Preload & afterload
- Arteriolar & venous dilation, cerebral vasodilation
- DOSE- 0.3–0.5 mcg/kg/min IV infusion, max – 10 mcg/kg/min
Ultra short acting -1-2min, t ½ 3-4 minutes
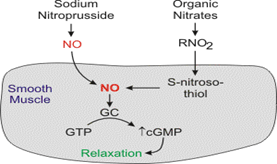
- Adverse Effect/Precaution-
- Cyanide & thiocyanate toxicity prolonged infusion,
- Thiosulfate – to prevent cyanide toxicity
- Bottle is covered with an opaque wrapping
- Continuous BP monitoring
- Use à Aortic dissection, Acute LVF
Nitroglycerin
- MOA- Greater preload reduction than afterload, Decreases coronary vasospasm
- DOSE- 5-100mcg/min, Titrate up 10mcg every 5 mins
Onset 2-5min, Half life – 4min
- Adverse Effect/Precaution- Headache, Tachycardia, Tolerance, Continuous BP monitoring
C/I- Head trauma/Cerebral haemorrhage, with PDE-5 inhibitors
- Uses – Acute HF, Acute coronary syndrome.
Oral/Sublingual Nifedipine
- MOA- Peripheral & coronary arteriolar dilator, Potential hypotension and/or reflex cardiac stimulation
Sudden uncontrolled & severe reductions in BP, may precipitate cerebral, renal & myocardial ischemic events
- “Inappropriate physician habits in prescribing nifedipine capsules in hospitalized patients”
- Cardiorenal Advisory Committee of FDA has concluded “that practice of administering SL/oral nifedipine abandoned because this is not safe nor efficacious1
Nicardipine
- MOA- L-type Ca++ channel blocker – selective Arterial vasodilator, Cerebral & Coronary vasodilatation
- DOSE- Start 5mg/hr IV infusion, titrate every 15min to max 15mg/hr
Duration of action 15-30min,
Adverse Effect/Précaution- Worsen/cause HF, Reflex tachycardia
- Uses – Ideal for CNS emergencies, Renal Disease
Clevidipine
- MOA- 3rd gen (L-type) CCB, arterial vasodilator FDA approval (2008), Injectable emulsion
- DOSE- Start 1-2mg/hr with rapid titration to max 32mg/hr
Ultra short t1/2 – 1 min, Duration of action 5-15min, PPB -99.9%
- Adverse Effect/Precaution- Atrial fibrillation, C/I – Allergies (soy & egg products), Defective lipid metabolism
- Uses – All HTN emergencies (Safe in Renal & Hepatic dysfunction)
Fenoldopam
- MOA- Peripheral Dopamine-1 agonist(DA1). 10 –fold more potent renal vasodilator than Dopamine
- DOSE- 01-0.3mcg/kg/min infusion, Max infusion rate – 1.6mcg/kg/min (Titratable, Predictable & Stable)
- Adverse Effect/Precaution- Tachycardia, Headache, Hypokalemia. Caution with glaucoma.
- Advantages- All HE, Renal insufficiency patients Strokes (combination with Nicardipine)
Hydralazine
- MOA- Direct arteriolar dilator, opening high conductance Ca2+-activated K+ channels
Delayed onset, Unpredictable hypotensive effect
- DOSE- Dose: 10-20 mg I V, repeated in 30 mins, 10-40mg IM. Not titratable
- Adverse Effect/Precaution- TACHYCARDIA, Drug-induced Lupus syndrome
Aggravation of angina, Sodium & water retention
- Advantages- Eclampsia
Enalaprilat
- MOA- Active component of Enalapril, ACE inhibitor
- DOSE- 1.25-5mg IV every 6hr. Difficult to titrate
- Adverse Effect/Precaution- Excessive fall in BP, C/I- Acute MI, Renal Disease, Pregnancy, Volume depletion
- Use – Acute LVF , Expensive
Esmolol
- MOA- Cardio selective β Blocker
- DOSE- Loading dose 500mcg/kg over 1 min, Infusion of 50-300mcg/kg/min
- Adverse Effect/Precautions- Bradycardia
C/I- 1st degree heart block, COPD, CKD
- Uses- Aortic Dissection, Cardioprotective in CVS emergencies
Labetalol
- MOA- Selective α1 and non-selective β blocker (1:7)
Maintains cardiac output, Cerebral, renal, coronary blood flow, Reduces SVR
- DOSE- 20-80mg IV Bolus every 10min, or infusion of 2mg/min to max of 300mg.
- Adverse Effect/Precautions- Exacerbate CHF, C/I – COPD, Heart Block, decompensated HF
- uses- PIH, Pheochromocytoma
Phentolamine
- MOA- α adrenergic blocker
- DOSE- Bolus 5-20mg IV every 5min,
- Adverse Effect/Precaution- Tachycardia, flushing, Postural Hypotension
C/I- use with PDE-5 inhibitors, Renal Impairment
- Advantages- Pheochromocytoma, Cocaine associated HPT crisis
Management of Hypertensive Emergency with TOD
Pulmonary Edema (LVF)
- Nitroglycerin 5 mcg/min.
- Sodium Nitroprusside (reduces preload) -0.3 to 0.5 mcg/kg/min
- IV Diuretic (reduces preload & afterload)- 40mg IV
- Morphine – Vasodilator & Sympatholytic
- Clevidipine infusion 1–2 mg/h, max 32 mg/h.
- Low EF à Avoid beta blockers/Negative inotropes
Acute Myocardial Infarction
- Reduce MAP by 20 -25% of baseline
- Nitrates should be given till symptoms subside or until DBP<100
- Drug of choice: Nitroglycerine 5 mcg/min, Labetalol (or Esmolol), Nicardipine – 5 mg/h
- Avoid Hydralazine – Increase myocardial O2 demand
Acute Aortic Dissection
- OK to aggressively reduce BP (<120/80)
- Reducing the shear stress on aortic wall
- Aim of treatment to reduce SBP as rapidly as possible down to 100-110 mmHg & to control tachycardia
- 1st Esmolol then Nitroprusside
- Hydralazine is C/I
Ischemic Stroke
- Blood Pressure -Systolic > 185 or diastolic > 110 mm Hg
- Labetalol 10 to 20 mg IV over 1 to 2 min may repeat x 1 or
- Nicardipine infusion, 5 mg/h, titrate up by 0.25 mg/h to max dose 15 mg/h
- Desired blood pressure obtained, reduce to 3 mg/h
- If BP not controlled or diastolic BP >140 mm Hg, consider IV sodium nitroprusside
Sympathetic crises
- PATHOLOGY- Pheochromocytoma, Monoamine oxidase inhibitor + tyramine, Cocaine/amphetamines overdose.
- GOAL- Reduce MAP by ~25% over several hours
- DOC- Phentolamine: 5-15mg IV bolus or drip 5-10mcg/kg/min
Beta-blocker- Labetalol (control tachycardia)
Benzodiazepines – Helpful in cocaine/amphetamine overdose
Pre-eclampsia and Eclampsia
- PATHOLOGY- Systemic arterial vasoconstriction (Including Placental)
- Defined as SBP = 140/90 mmHg or greater, OR a 20 mmHg rise in SBP or 10 mmHg rise in DBP from baseline
- Restlessness & hyper-reflexia , seizures, proteinuria
- GOAL- Delivery of the fetus and placenta
- DOC- MgSO4: 4-6gm over 15 minutes IV, drip 1-2gm/hr
- Hydralazine: 5-10mg IV, drip 5-10mg/hr
- Labetalol: 20mg IV, repeat prn q 10 mins, drip 1-2mg/min
Intracerebral Hemorrhage
Rise in BP due to increased ICP & irritation of ANS
- GOAL- Treatment based on clinical/radiographic evidence
Raised ICP – MAP<130 (1st 24hrs)
No raised ICP – MAP<110
To prevent re-bleeding & reduce edema.
BP >180/105 mmHg , benefit from gradual 20-25% reduction in BP
- DOC- IV Nicardipine 2mg bolus, then 4-15mg/hr (treat SAH )
Nimodipine PO 60mg q 4hr (to reverse vasospasm)